
 |
Manual |
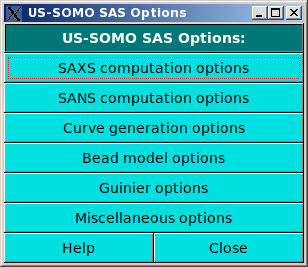
In this module you can set/change the parameters used by the SAXS/SANS (SAS) and MALS Data Processing and Simulation Module. The module has been split up into several sub-modules, as shown in the above image. The sub-menus can be accessed by clicking on their names.

In the SAXS Computation Options: section, the first entry that can be set/changed is the Water electron density (e / A^3): (default: 0.334 e/A3).
Next comes the choice between the computational methods offered: full Debye ("F-DB"), Debye with spherical harmonics ("SH-DB"), a fast methods based on FoXS (Schneidman-Duhovny et al., Nucl. Acids Res. 38, W540-W544, 2010), whose code is only available for Linux operating systems ("quick" Debye, "Q-DB"), and Crysol (Svergun et al., J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 768-773, 1995). If "Q-DB" is selected, it is possible to have at the same time the computation of the P(r) vs. r function by ticking the "P(r)" checkbox. In particular:
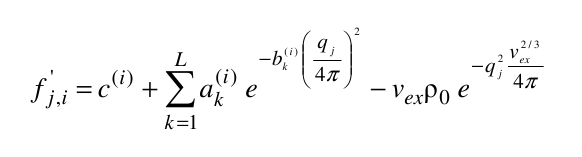
where ak(i), bk(i), and c(i) are the pre-exponential terms, the exponential (Gaussian) terms, and the constant term, respectively, of the atomic form factors taken from the International Tables for Crystallography and stored in the SAXS coefficients table, L is the number of Gaussian terms used (4 or 5, user-selectable in the SAS Miscellaneous Options menu, see below; for the 5 Gaussians, see Waasmaier and Kirfel, Acta Cryst. A51:416-431, 1991; Yonekura et al., IUCrJ 5:348-353, 2018), vex is the excluded volume of each atom retrieved from the atom definition table, and ρ0 is the solvent electron density, stored in the US-SOMO SAXS calculation options (default: water, 0.334 e/Å3). If implicit hydrogens are used, as is typical for most structures derived from X-ray crystallography studies, then structure factors derived from a Debye computation utilizing typical hydrogen positions replace the atomic form factors. The vex for non-H atoms stored in the somo.atom file already includes the H atoms bound to every particular group defined there (e.g., C4H3 vex = 31.89 Å3, C4H0 vex = 16.44 Å3). The Ij are then computed for each qj as:
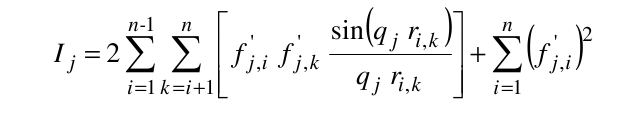
where ri,k is the distance between the centers of atoms i and k.
Next come a series of entries where various parameters can be set:
In the Quick Debye: Bin size. Smaller bin sizes increase accuracy at the cost of increased computational time. See the FoXS paper reference for details. The default value is that used in the standard FoXS method.
In the Quick Debye: Modulation. The modulation effects the exponential decay of a point scatterer extended from the intensity at q = 0 (I(0)). See the FoXS paper reference for details. The default value is that used in the standard FoXS method.
The next three entries set some Crysol options (the first affects also the SH-DB method):
SH/Crysol: Maximun order of harmonics (default: 15). Increase this number as the size of the structure grows (max for the current Crysol implementation: 40).
Crysol: Order of the Fibonacci grid (default: 17). Increase this number as the size of the structure grows (max for the current Crysol implementation: 18)
Crysol: Contrast of the hydration shell (e/A^3): (default: 0.03 e/A3). Set this parameter to "0" if you want to run Crysol on a structure with explicit hydration waters.
Five checkboxes follow, grouped under Crysol options::
Automatically load difference intensity (default: on). After a Crysol computation, the difference intensity data will be loaded in the graphic window.
Support version 2.6 (default: on).
Support version 3.1+ (default: off).
Shell water (3.1+ only) (default: off). This is a relatively recent new Crysol feature allowing the representation of hydration waters as dummy beads placed on the bio-macromolecule's exterior surface, and their inclusion in the I(q) calculations (see Franke et al., J. Appl. Cryst. 50:1212-1225, 2017).
Crysol: Explicit hydrogens (default: off). By default, Crysol uses implicit hydrogens considered as part of the bound atom and explicit hydrogens are removed. If you wish to use explicit hydrogens specificed in your pdb, then select this option.
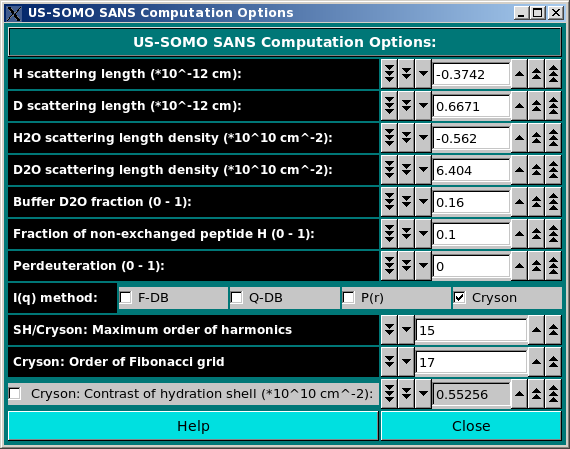
In the SANS Options: section, several parameters can be controlled:
b(Y)i = b(0)i + n(HExch)i * Y * [b(D) - b(H)] * [ 1- f(NHExch)i]
where b(0)i are the neutron scattering lengths of the non-H atoms at Y = 0 and n(HExch)i are the number of exchangeable H attached to them (both tabulated in the hybridization table), b(D) and b(H) are the D and H scattering lengths, respectively, and f(NHNExch)i is the fraction of non-exchanged peptide bond H (which is 0 for all atoms except for the peptide bond N atom), all as defined in this panel (see above). The perdeuteration field is used by Cryson (see below).
As for the SAXS Computation options panel, we have listed a series of alternative methods for the computation of the SANS I(q) vs. q curves. However, only Cryson (Svergun et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 2267-2272, 1998) is presently (as of June 2024) active.
The maximum number of harmonics and the order of the Fibonacci grid can be set in the corresponding fields for Cryson. Regarding the Cryson: contrast of the hydration shell field, it is automatically computed from the D2O fraction (see Cryson manual), but the value proposed can be overridden by checking the checkbox provided and entering a different value.
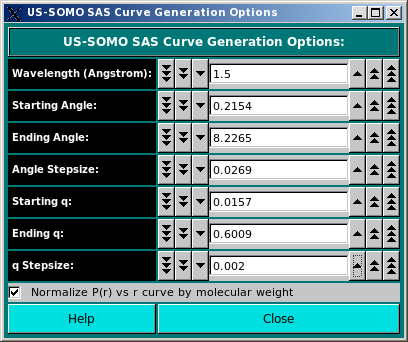
The SAS Curve Generation Options: section contains fields whose values are used in the simulation of either a
SAXS or a SANS curve.
Enter either the X-ray or neutron wavelength in the Wavelength (Angstrom): field (default: 1.5 A for
SAXS; for SANS, an usual value is 6 A).
The span and point density of the simulated curve can be controlled by entering appropriate values in the
Starting Angle, Ending Angle, and Angle Stepsize fields, or in the
corresponding Starting q, Ending q, and q Stepsize fields, where the
transformation from angle units to scattering vector q units is automatically carried over by the program.
Default values are 0.001 to 0.6 A-1 q range with a 0.015 stepsize, corresponding to an
angular range of 0.014 to 8.214 degrees with a 0.2 degrees stepsize for a wavelength of 1.5 A.
The Normalize P(r) vs r curve by molecular weight is selected by default. Deselecting it will cause the P(r) vs. r curves to be normalized only by their areas.
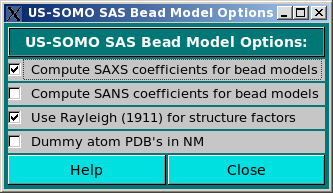
This module allows selecting the computation of the SAXS and/or SANS coefficients when generating bead models from atomic scale structures (Compute SAXS coefficients for bead models and Compute SANS coefficients for bead models checkboxes), and to optionally use the Rayleigh (Rayleigh, Proc. Royal Soc. London A84:25-46, 1911) structure factors for spheres of uniform electron density (Use Rayleigh (1911) for structure factors checkbox). This procedure is still under development, and will be fully described elsewhere.
The Dummy atom PDB's in NM checkbox is used when uploading bead models whose scale units are not in Å but in nm, like some DAMMIN/DAMMIF-generated models.

In the SAS Guinier Options menu, the options controlling the Guinier analysis of SAS data can be set, and the various operational modes can be then launched. After setting/revising the options and the parameters, three different Guinier analyses can be launched by pressing "Process Guinier" (conventional Guinier, ln[I(q)] vs. q2), "Process CS Guinier" (cross-section Guinier for rod-like particles, ln[q I(q)] vs. q2), or "Process TV Guinier" (transverse Guinier for disk-like particles, ln[q2 I(q)] vs. q2), respectively.
The general Guinier options that can be set/modified are:
The specific Guinier, CS Guinier and TV-Guinier options that can be set/modified are:
Note that by changing a value in the q fields, the corresponding value in the q2 fields is automatically updated, and vice-versa.
The MW and M/L computation options section deals with the parameters that are necessary to perform a correct calculation of <M>w or <M/L>w/z or <M/A>w/z.
Note: from the July 2024 release, the calculations necessary to put the experimental data on an absolute scale can be done directly in the HPLC/KIN module, generating what we have called "I#(q)" and "I*(q)" datasets/files. These files will be automatically recognized and no further calculations will be performed on them, except using an entered concentration for the "I#(q)" datasets.
Otherwise, the conversion from the corresponding experimental <Iexp(0)>w value is done by first putting the data on an absolute scale by normalizing for the intensity extrapolated to 0 scattering angle of a known standard, 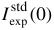 , according to:
, according to:
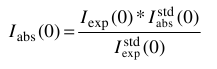
Then the reduced 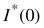 in g mol-1 are obtained as:
in g mol-1 are obtained as:
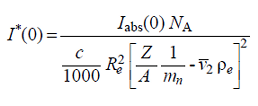
where NA is Avogadro's number, c is the sample concentration [mg ml-1], Re is the diffusion length of the electron [cm], mn is the nucleon mass [g] (note: from 2019, this value by default is taken as 1/NA), 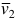 is the partial specific volume of the particle [cm3 g-1], ρe is the solvent electron density [e/cm3], and Z and A are the number of electrons and of nucleons, respectively, in the particle, whose ratio is usually taken as a constant specific for each class of biomacromolecules.
is the partial specific volume of the particle [cm3 g-1], ρe is the solvent electron density [e/cm3], and Z and A are the number of electrons and of nucleons, respectively, in the particle, whose ratio is usually taken as a constant specific for each class of biomacromolecules.
If a series of I(q) SAXS curves have been uploaded in the SAS module (for instance, from the HPLC/KIN module), it is possible to set/modify their associated parameters by pressing the Set Curve Concentration, PSV, I0 standard experimental button (see here). As stated above, for already fully pre-processed I*(q) datasets, proper values for these parameters were already employed, and will just be shown by accessing this module. The same partially holds for I#(q) datasets, for which a c value can instead be entered.
When no parameters are entered via the Set Curve Concentration, PSV, I0 standard experimental module, the program will utilize the values as set in this section of the Guinier Options module, which also contains the other parameters necessary for the computation of the <M>w or <M/L>w/z or <M/A>w/z values. In particular:
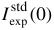 experimental value and its theoretical value under the same experimental (T, pressure) conditions will be used to normalize the SAXS data.
experimental value and its theoretical value under the same experimental (T, pressure) conditions will be used to normalize the SAXS data.
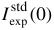 is not associated with the data, or entered via the Set Curve Concentration, PSV, I0 standard experimental module. (Default: 0.01633 a.u.; this value is set equal to the default value for water at 20 °C, the standard used in US-SOMO, see below).
is not associated with the data, or entered via the Set Curve Concentration, PSV, I0 standard experimental module. (Default: 0.01633 a.u.; this value is set equal to the default value for water at 20 °C, the standard used in US-SOMO, see below).
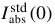 for the chosen standard. The default value (0.01633 cm-1) is that for H2O at 20 °C.
for the chosen standard. The default value (0.01633 cm-1) is that for H2O at 20 °C.
After properly setting all options/parameters, the computations of the three different Guinier data analysis processes can be launched by pressing either the Process Guinier, or the Process CS Guinier, or the Process TV Guinier buttons.

In the SAS Miscellaneous Options menu, several controls and limits can be set.
In order to properly compute the I(q) vs. q and P(r) vs. r curves, the SAS module utilizes the atom definition (default: somo.atom), hybridization (default: somo.hybrid) and SAXS coefficients (default: somo.saxs_atoms) tables.
Different tables can be selected by pressing the Load Atom Definition File, Load Hybridization File, and Load SAXS Coefficients File buttons. See the main help for further explanations on the content and use of these tables.
Next come a series of checkboxes:
The Excluded volume scaling field allows to modify by a % value the excluded volumes of the non-water atomic groups as tabulated in the atom definition table.
Pressing the Clear remembered molecular weights button will erase stored MW from the program's memory.
A different q range can be entered in the I(q) curve q range for scaling, NNLS and best fit (Angstrom) two fields.
Two new checkboxes where added starting from the March 2023 release:
This document is part of the UltraScan Software Documentation
distribution.
Copyright © notice.
The latest version of this document can always be found at:
Last modified on June 25, 2024.